Glaucoma Laser Surgery Treatment
How is laser eye surgery for glaucoma performed? In the treatment of glaucoma, a laser beam is initially used to treat acute glaucoma crises. In glaucoma, the laser is applied to the eye’s filter-like outflow passages to help with fluid drainage. There are several kinds of lasers used to treat eye disorders. The laser utilized in the treatment of myopia differs from the laser utilized in the treatment of diabetes. Similarly, lasers utilized in cataract procedures, the reduction of posterior capsule opacity following cataract surgery, the retinal therapy of preterm infants, and acute angle closure are distinct.
The “Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty (SLT)” surgery is used to treat glaucoma with a laser. The FDA approved the Q-switched FD Nd:YAG laser, which has a wavelength of 532 nm, in 2001 and has gained popularity globally since 2005.
Laser treatment of glaucoma
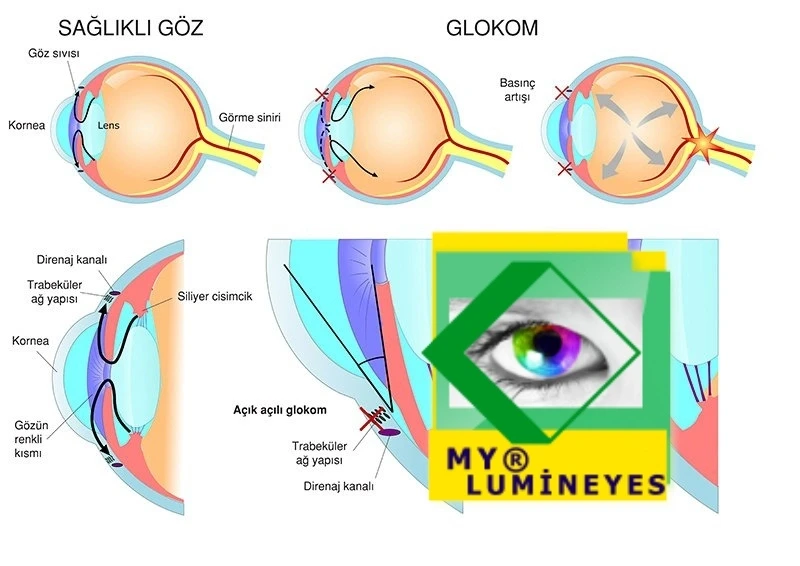
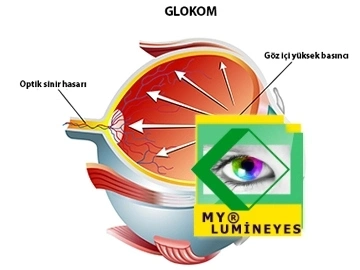
Glaucoma is an extremely difficult eye condition. Typically, it is chronic and progressive in nature. This disease represents the second-leading cause of blindness in the world. It manifests in various ways and, if not detected in a timely manner, can cause severe and irreversible damage in a subtle and quiet manner. An injury capable of causing blindness In particular, it is produced by a higher internal pressure than the eye can ordinarily withstand.
The most revolutionary laser surgery for glaucoma is selective laser trabeculoplasty (SLT), which has been accessible around the world for the past 20 years but is still underutilized.
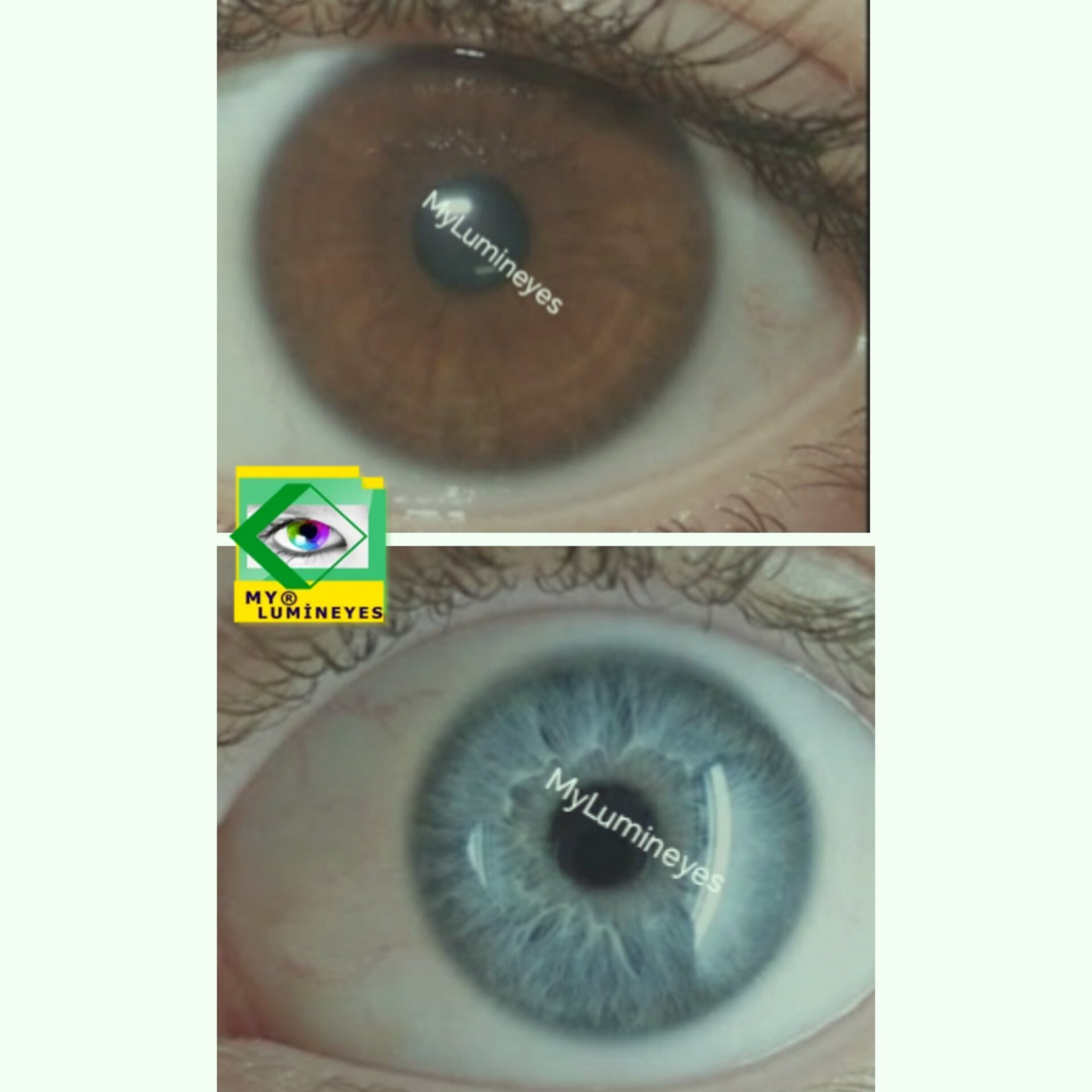
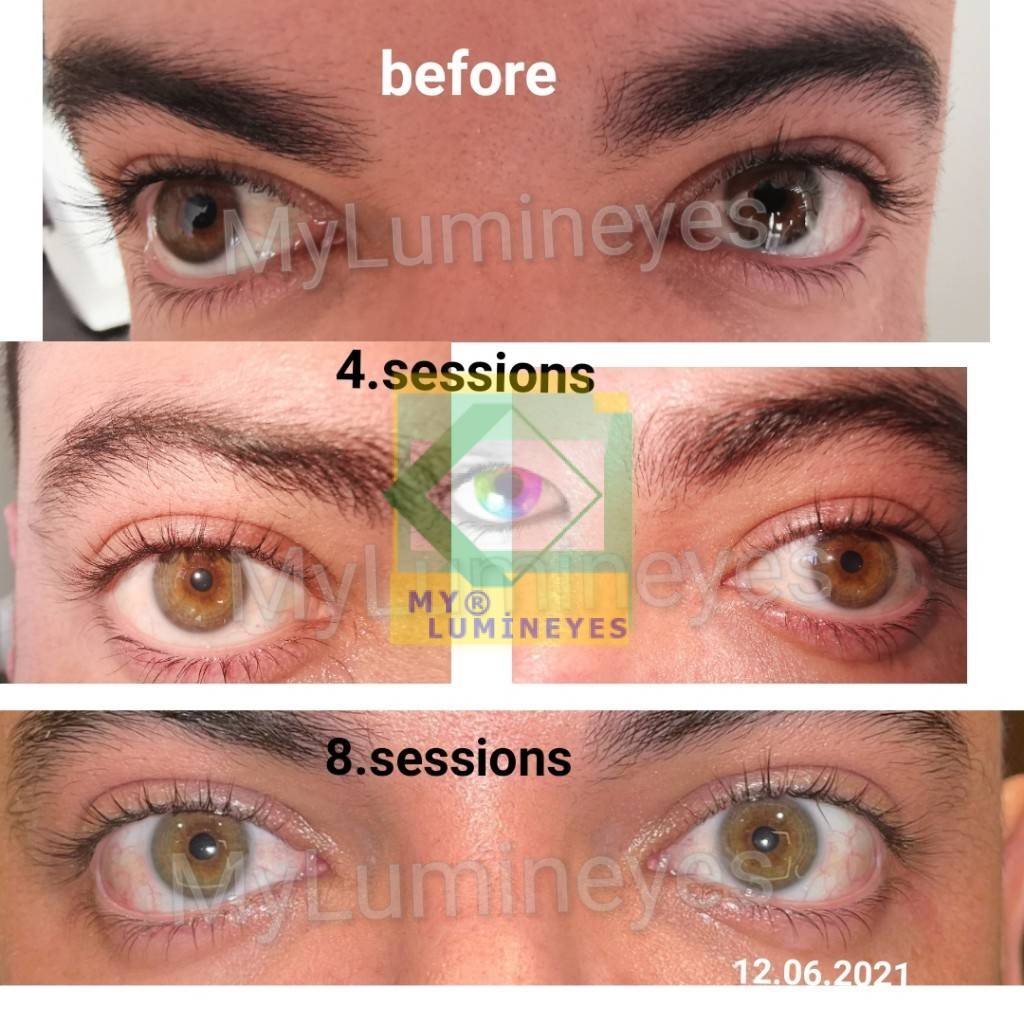
When treating closed-angle glaucoma, Yag laser iridotomy or trabeculoplasty laser surgery are used.It can be used in a number of ways to avoid acute glaucoma in people with open-angle glaucoma. Dr. Mustafa Mete states that the Lumineyes laser eye color change procedure, which will be used for laser color change surgery in 2021, reduces intraocular pressure and can even be used in the treatment of glaucoma, contrary to what is known.
Laser therapy can effectively cure glaucoma in specific cases.
The laser is a powerful and tightly concentrated light source that facilitates the creation of innovative and reliable therapeutic methods. There are relatively effective, less-invasive methods available for managing glaucoma. Hospitalization is not required for outpatient laser surgery.
After a drop of anesthetic is administered, rendering the process painless, the patient sits and rests against the chin support (as in the slit lamp examination). After putting gel on the eye, a contact lens is put in, and laser treatment is given for a few seconds or minutes, depending on the type of laser and the treatment being done.
There are a variety of laser therapy types, each with its own indications and contraindications.
Consequently, it is essential to precisely identify patients who may benefit from various forms of treatment. Laser therapy tries to control intraocular pressure by reducing or eliminating the need for eye drops that cause irritation or by avoiding or putting off surgery.
It has emerged as a reliable and effective technique for glaucoma.
This treatment is considered as a revolution in the treatment of eye pressure and is applied to the patient in a simple and comfortable way. SLT eliminates the need for medication for glaucoma patients and may not even require surgery.
- The patient is free of side effects and high drug costs due to glaucoma medications, and does not experience drip tension at certain hours.
- SLT laser stimulates the body’s own immune system and reduces intraocular pressure.
- It is the laser method used in intraocular pressure elevations due to open angle glaucoma.
- offers easy, reliable and numerous sessions that can last for 1-2 minutes.
- It reduces the intraocular pressure without damaging normal tissues by affecting the pigments accumulated or present in the drainage channel of intraocular fluid.
What Are The Advantages Of The Selective Laser Method?
- It stimulates the production of natural cells and increases the output of intraocular fluid by opening blocked channels.
- It is selective. selectively targets melanin-rich cells in the trabecular network.
- Safe: no major complications reported yet.
- The short pulse duration of the SLT therefore minimizes the thermal damage of the tissue in the trabecular network, eliminating the possibility of thermal damage.
- It is reproducible and can be rebuilt without causing complications.
What is the laser surgery for glaucoma?
Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty (SLT) is a recently developed laser procedure for lowering intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma. Low-dose laser energy is supplied to the blocked channels via SLT. This eliminates the pigment-containing cells (melanin) and causes them to vanish.
How is laser glaucoma therapy administered?
At the commencement of the procedure, anesthetic drops are used to numb the patient’s eye. In this manner, the patient does not experience any pain or discomfort during the treatment. Following numbness, laser therapy is administered for 40 to 1 minute in the trabecular region, where intraocular fluid is expelled.

Laser eye surgery for glaucoma on the iris melanin layer
When medical therapy is unsuccessful or ineffective, laser or surgical procedures may be used. The goal of these therapies is to preserve the patient’s residual vision rather than to improve it. The treatment for the narrow-angle type that occurs during a crisis is extremely urgent, and it may be necessary to begin with a laser to create a hole in the iris tissue. Depending on the type of glaucoma, laser eye surgery may be recommended.The microscopic canal system is treated immediately in glaucoma with an open angle. Laser therapy is used to control intraocular pressure by altering the canal system (trabeculoplasty).
To treat angle-closure glaucoma, laser iridotomy is used to create a hole in the iris tissue and adjust the flow of aqueous humor through the canal system.
Glaucoma accounts for 13.5% of all cases of blindness worldwide. It is an ocular neuropathy condition that can lead to peripheral vision loss before causing complete vision loss. With this condition, optic nerve fibers are destroyed progressively. Vision loss can be avoided by halting its development if detected early. Glaucoma, one of the causes of visual loss, is typically gradual and subtle. Delay in diagnosis results in irreparable visual impairment.
Laser therapy at the angle of the iridocornea
There are various laser types that can be used for this purpose: In the past, argon laser trabeculoplasty (ALT) was utilized. Currently, the YAG laser, specifically selective laser trabeculoplasty (SLT), is the recommended treatment option. The YAG laser precisely targets the pigmented cells of the trabeculae, minimizing the influence on adjacent structures
The use of selective laser therapy (SLT) in the management of ocular hypertension and glaucoma
Laser trabeculoplasty is an effective treatment for open-angle glaucoma. The objective is to enhance the absorption of fluid by targeting a laser beam to the angle of the anterior chamber, which is responsible for fluid absorption. This procedure is performed on an outpatient basis. Generally, its utility is restricted to a duration of two to three years. Laser therapy for glaucoma can be used to achieve various goals. In severe glaucoma crises, prompt laser therapy is quite useful
The amount and frequency of drops in open-angle glaucoma can be lowered even if therapy is not halted by developing tiny holes in the trabecular area where the blockage is present. A very reduced pulse can also be used in the discharge tubes, which is a recent approach. So, how are selective laser trabeculoplasty (SLT), ECP, and diode laser techniques used to treat glaucoma?
What is the cost of laser treatment for glaucoma?
With selective laser trabeculoplasty, the intraocular pressure is decreased by correcting the blockage in the channels that supply the outflow of intraocular fluid. Thus, SLT affects only the pigmented cells on iris and not the nonpigmented cells or connective tissue in these channels. Due to the fact that it does not impact the non-pigmented cells and connective tissue, the wound does not heal. This guarantees that clear channels remain open and do not close. Laser treatment for glaucoma can vary between 300 and 750 euros per session.
This trait sets SLT apart from other laser therapy techniques. Because of this advantageous feature, when selective laser trabeculoplasty is done on patients who have failed argon laser trabeculoplasty, more than half of them see improvement.
Difference between SLT and ALT
The main advantage of Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty over Argon Laser Therapy (ALT), which was used prior to 2000, is that it does not harm the anterior chamber angle and so allows for repeated surgeries. It is a quick outpatient operation.
SLT (Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty) What is SLT?
It has developed into a dependable and successful glaucoma treatment method. This procedure is considered a revolution in the treatment of ocular pressure since it is straightforward and pleasant for the client. SLT reduces the need for glaucoma medicines and may potentially eliminate the necessity for surgery.
The patient is free of glaucoma prescription adverse effects and excessive drug prices, and he does not endure outflow pressure at specific times. Selective lasers enhance the immune system and lower intraocular pressure.
SLT is the laser technique used to treat intraocular pressure increases caused by open-angle glaucoma.
This laser provides simple, dependable, and numerous 1-2 minute sessions.Finally, it lowers glaucoma without harming normal tissues by changing pigmentation deposited in or present in the ophthalmic fluid drainage system.
SLT, also known as selective laser trabeculoplasty, is a simple yet highly efficient technique for lowering intraocular pressure in glaucoma patients. Glaucoma-STL is a gentle alternative to traditional glaucoma treatment. It takes less than five minutes for your eye doctor to do it in their office.
The purpose of trabeculoplasty, a type of laser surgery for glaucoma, is to facilitate the drainage of aqueous fluid from the eye. This reduces the eye’s pressure.
This procedure treats the iridocorneal angle at the level of the trabeculae. Using specialized gonioscopic-angle lenses, laser points should be focused at the junction of pigmented and nonpigmented trabeculae. The decrease in intraocular pressure (IOP) is caused by the laser’s mechanical and biological effects. This type of laser is used to treat high-risk cases of primary open-angle glaucoma, pigmentary glaucoma, pseudoexfoliative glaucoma, and ocular hypertension.
What exactly is a diode laser for treating eye pressure or glaucoma?
The laser beam is initially used to treat acute glaucoma crises and to keep the opposite eye from developing a glaucoma attack. with situations of chronic glaucoma, the laser is focused on the filter-like outflow channels to aid with fluid drainage from the eye.
Endoscopic Laser Treatment for Glaucoma (ECP)—Endoscopic Laser Treatment for Eye Tension
ECP decreases intraocular pressure by lowering intraocular fluid production. Since the channels that allow intraocular fluid to escape the eye are clogged in glaucoma patients, intraocular fluid collects and eye pressure rises. Endoscopic laser treatment, also called ECP, stops the body from making intraocular fluid by removing some of the tissues (ciliary body) that make intraocular fluid. This lowers eye pressure. In reality, the idea of “lowering eye pressure by reducing the production of intraocular fluid” is quite old. Until recently, high-temperature therapy (diathermy) and cold therapy (cryotherapy) were used for this purpose.
This procedure, known as diode laser, is used on individuals whose ocular pressure cannot be properly decreased by drops or surgery.
A local anesthetic is used for laser treatment. Ocular tension is successfully lowered without the need for hospitalization. It takes around five minutes. The aqueous fluid production process is disturbed in diode laser therapy by providing energy to the ciliary body, lowering ocular stress. It is a very efficient approach for lowering ocular pressure.
with diode laser glaucoma treatment
This method, called diode laser, is applied to patients whose eye pressure cannot be reduced sufficiently by drops or surgery. Laser application is performed with local anesthesia. Eye pressure is reduced successfully without the need for hospitalization. It takes about five minutes. In diode laser treatment, the aqueous fluid production process is disrupted by applying energy to the ciliary body, thereby reducing eye tension. It is a very effective method for reducing eye pressure.
Laser therapy for glaucoma:
In the treatment of glaucoma, patients who do not react satisfactorily to medication therapy have the option of undergoing laser therapy before surgery. Glaucoma treatment involves argon laser application to the trabecular meshwork. Laser treatment can normalize intraocular pressures that are not too elevated. This treatment can decrease eye pressure by as much as 30%. Typically, the duration of the impact is between two and three years, and it diminishes dramatically within five years. The relationship of glaucoma with food has not been determined yet.
The intraocular pressure may then increase again. Therefore, laser therapy is preferable only for pressures up to 26 mmHg in patients who do not cooperate with pharmacological treatment and who cannot undergo surgery.
In addition, “lumineyes laser eye color change surgery” is applied with very high success for the solution of eye color change problems in pigment dispersion syndrome and heterochromia.
In addition, we use laser methods in the treatment of glaucoma due to pigment dispersion syndrome or in the treatment of heterochromia patients. For the first time in the world, we have succeeded in making the different eye colors of heterochromia patients equal. Without a doubt, lasers will continue to break new ground in eye surgeries and treatments. We can easily say that we will continue to be a pioneer in eye treatments with laser.
Laser Treatment for Glaucoma
In glaucoma, laser treatment can be used for a variety of purposes.Timely laser treatment is very beneficial in acute glaucoma crises. In open-angle glaucoma, the number and frequency of drops can be reduced even if the treatment is not interrupted by making small holes in the trabecular region where the obstruction is present. Or, as a newer technique, a very low-energy laser can be applied to the discharge channels. On this page, we will tell you how glaucoma is treated with selective laser eCP and diode laser methods.
Glaucoma Endoscopic Laser Treatment
ECP lowers blood pressure by partially inhibiting the generation of eye fluid. Endoscopic laser treatment, or ECP, lowers intraocular flow formation by partly eliminating the tissues (the ciliary body), which is the site of ophthalmic fluid formation, with a laser and lowering eye pressure. In truth, the concept of lowering eye pressure by decreasing intraocular fluid production is quite ancient, and for this goal, diathermy (high-temperature therapy) and cryotherapy (cold-freeze treatment) were employed for the first time, and a diode laser was recently substituted.
Either of these approaches cannot properly lower eye pressure or, on the contrary, can reduce eye pressure excessively, resulting in eye reduction and vision loss.
The ciliary body, which generates eye liquid and is the focus of our therapy, is positioned behind the “sclera,” or white area of the eye, and is difficult to view with traditional procedures. In the ECP procedure, an endoscopic camera that penetrates the eye is utilized to locate and burn “target cells” in the eye that conventional treatments cannot see.
ECP lowers blood pressure in part by stopping the production of fluid inside the eye.
Either of these methods can’t lower eye pressure enough or, on the other hand, can lower eye pressure too much, which can cause the eyes to shrink and cause vision loss.
ECP is a much more reliable and controlled treatment than other ways to stop fluid production.
The ciliary body, which is the objective of our treatment and produces eye fluid, is hidden behind the “sclera,” the white area of the eye, and is difficult to see with traditional procedures. The ECP approach uses an endoscopic camera that penetrates the eye to locate and burn “target cells” in the eye that traditional procedures cannot see.
Iridotomy
Aqueous humor is created by the ciliary body and flows through the pupillary foramen from the posterior chamber (behind the iris) to the anterior chamber of the eye (in front of the iris). By way of the trabeculae and Schlemm’s canal, it then enters the main circulation. In angle-closure glaucoma, the increased pressure in the posterior chamber pushes the iris forward, obstructing the trabeculae. Iridotomy has a therapeutic impact on lowering intraocular pressure in cases of narrow-angle glaucoma and acute glaucoma, as well as in some cases of mixed glaucoma and phacomorphic glaucoma with pupillary block.
Patients with an occluded angle or a closed angle of more than 180 degrees can be kept from getting an acute or long-term corner closure.
Typically, laser iridotomy is performed peripherally so that the upper iris can be concealed by the upper eyelid. In certain instances, two supero-lateral punctures may be indicated. Occasionally, multiple types of lasers (argon or yag) can be combined. The choice of laser type is influenced by the iris’s color and thickness. However, iridoplasty is not recommended if the iris is flat or there is a lot of anterior peripheral synechia.
Iridoplasty by a laser
Iridoplasty is performed by arranging laser spots in a ring within the peripheral iris to detect a superficial scar that narrows the iris stroma and enlarges the iridocorneal angle. The actual principle is to open the circumferential corner to limit the possibility of corner closure. This treatment is indicated in situations of plateau iris, in anticipation of laser trabeculoplasty in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma, and in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma who do not react to pharmacological therapy and cannot have peripheral iridotomy (e.g., due to the presence of corneal edema).
On the other hand, iridoplasty is not a good idea if the iris is flat or if there is a lot of anterior peripheral synechia.
The treatment results in the formation of four to ten scars in each primary quadrant, measuring between 200 and 500 microns in size. Post-surgical patients may experience a temporary increase in intraocular pressure. Its moderate risk of iritis necessitates occupational monitoring. In rare cases, this medication may cause the iris to constrict and the pupils to dilate.