Laser Eye Color Change Procedure
Book a Clinical Evaluation
This page is the official clinical overview of the Laser Eye Color Change Procedure.
To check eligibility and receive a personalized plan, request a clinical assessment.
Medical Director: Dr. Mustafa Mete, MD |
Location: Istanbul, Turkey
Quick Summary
- Non-incisional medical laser approach — no implants, no corneal pigmentation, no intraocular entry
- Gradual biological timeline — brightening develops over weeks as pigment clears naturally
- Staged laser sessions — brief sessions with step-by-step clinical assessment
- Safety-focused monitoring — suitability and response are evaluated throughout the process
- Cost, sessions & medical risks
Laser eye color change is currently the only non-incisional medical approach studied for cosmetic iris lightening.
Laser Eye Color Change is a non-incisional medical procedure designed to gradually lighten the natural iris pigment through a controlled, melanin-targeted photochemical process. The Lumineyes™ Method has been clinically developed and performed by Dr. Mustafa Mete for more than a decade, working within the eye’s natural biological framework rather than altering or replacing anatomical structures. By selectively reducing stromal melanin density, the procedure allows the eye’s existing color characteristics to become more visible over time.
Unlike cosmetic intraocular implants or corneal pigmentation techniques, no foreign material is introduced into the eye, and no structural tissue modification is performed. The approach prioritizes biological response, gradual change, and anatomical preservation. The purpose of this page is to serve as a comprehensive clinical reference for laser eye color change, including how the procedure works, patient suitability, safety considerations, expected outcomes, and long-term biological behavior.
Procedure Overview (Clinical Snapshot)
| Sessions | Staged sessions, individualized after evaluation |
|---|---|
| Average Timeline | Gradual biological brightening over weeks |
| Expected Result | Progressive pigment lightening (final shade varies) |
| Risk Level | Medically supervised procedure (case-dependent) |
| Follow-up | Clinical monitoring scheduled throughout stages |
How Laser Eye Color Change Works
This section explains how laser eye color change works within a controlled clinical framework, as part of the overall medical evaluation described on this page.
The technique uses a specific, low-energy laser wavelength directed toward the iris stroma. The laser interacts with melanin granules and initiates a controlled biological response. Over a period of weeks, these pigment particles are broken down and gradually cleared through natural metabolic pathways. As stromal melanin density decreases, the iris becomes lighter and more reflective, revealing natural underlying patterns.
This process is fundamentally biological. The laser does not cut, penetrate, or remove tissue. Instead, it relies on the eye’s own cellular and metabolic mechanisms. Because every iris is unique, outcomes vary based on pigment type, distribution, and individual physiological response.
- No incision — the laser does not create a wound.
- No implant — nothing is placed inside the eye.
- No alteration of internal structures — the anatomy remains unchanged.
- Predictable patterns of melanin modulation have been observed clinically, although individual response varies and is evaluated throughout the staged treatment process.
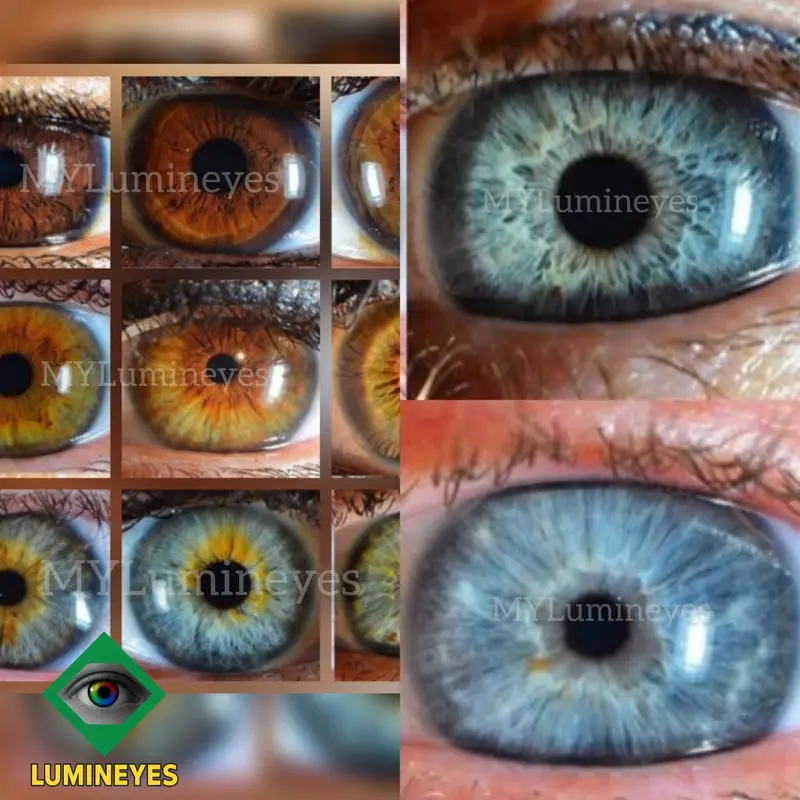

Why This Method Is Different
Laser eye color change is distinct from other approaches because it works with natural iris pigment rather than adding artificial color or modifying corneal tissue. This provides several important advantages:
- No foreign material is introduced, minimizing risks associated with implants.
- No structural invasion of the cornea or internal eye tissues.
- Natural appearance — the final result reflects the real iris texture.
- Gradual, controlled progression allows for clinical monitoring.
- Minimal downtime — most patients resume activities the same day.
Who Is a Suitable Candidate?
Laser eye color change is suitable for selected individuals following a comprehensive ophthalmic evaluation. Suitability is determined by iris pigmentation characteristics, overall ocular health, and absence of conditions that may interfere with healing or pigment modulation.
Ideal candidates typically meet the following criteria:
- Healthy cornea and anterior segment anatomy
- Adequate stromal melanin density for effective modulation
- No uncontrolled or advanced glaucoma
- No history of recurrent inflammation (uveitis)
- Stable intraocular pressure
- No active infection or ocular surface disease
Patients with uncertain suitability may require additional testing, such as endothelial evaluation, angle assessment or pigment distribution mapping.
Clinical Evidence and Academic Perspective
For a detailed clinical discussion of selective laser iris depigmentation, see our peer-reviewed clinical overview:
👉 Selective Laser Iris Depigmentation – Clinical Perspective
Clinical FAQ (Booking, Cost, Sessions)
How much does the procedure cost?
Cost depends on iris pigment density and the number of required sessions. A clinical evaluation is required to confirm an individualized plan.
How many sessions are needed?
Sessions are staged and determined after examination. The protocol is customized based on iris response and safety monitoring.
Am I eligible?
Eligibility is confirmed after ophthalmic assessment (ocular health, iris structure, and risk factors).
How do I book an evaluation?
Use the booking form to request a clinical evaluation. Our team will reply with the next steps.
How long is recovery?
Most patients resume normal activities the same day. Follow-up timing is individualized and explained during evaluation.
Indications & Limitations
The procedure for changing eye color with lasers is intended for eyes with adequate stromal pigment, stable anterior segment anatomy, and no active inflammatory or degenerative conditions. It is not suitable for individuals with congenital iris defects, advanced endothelial compromise, uncontrolled diabetes, those using antipsychotic drugs, or uncontrolled intraocular pressure. Clear anatomical limits and correct patient selection remain essential for achieving a predictable and safe biological response.
What Happens During the Procedure?
The procedure is conducted under medical supervision and typically consists of a series of brief laser sessions. Each session targets a specific region of the iris, ensuring even distribution and controlled pigment modulation.
- Session duration: generally a few minutes per eye
- Total number of sessions: varies based on baseline pigmentation and desired brightness
- Comfort: most patients report mild or no discomfort
- Clinical monitoring: the eye is examined at each stage to assess response
The brightening effect is not immediate. The biological clearance of pigment occurs gradually, with visible changes appearing over several weeks.
Expected Results and Timeline
The progression of brightening follows a natural curve. Early results typically show subtle increases in clarity and reflectivity. Over successive weeks, the iris becomes noticeably lighter. The pace of change depends on individual pigment composition and the eye’s natural metabolic rate. For this reason, laser eye color change outcomes are evaluated over time rather than defined by a fixed final shade.
Many patients observe:
- Increased iris reflectivity
- Enhanced definition of natural iris fibers
- Gradual brightening over weeks to months
- Stable appearance after the modulation phase is complete
Because the process works with natural pigment, results retain the unique characteristics of the patient’s iris rather than an artificial, uniform color. No specific final shade can be predicted, as outcomes vary according to each eye’s unique biological response.
Understanding the Limits of Predictability
No exact final eye color can be guaranteed. Each iris responds according to its own pigment distribution, metabolic clearance rate, and stromal texture. Biological variability means that simulations can illustrate general brightness expectations but cannot replicate an exact final shade. The outcome always reflects the patient’s natural iris architecture rather than producing a uniform or artificial appearance. You can check from here “Lumineyes laser eye color change” results : Before–After clinical examples
MyLumineyes® XTRA
XTRA is an advanced clinical protocol preferred by many patients. It is enhanced application of the staged Lumineyes™ laser approach. XTRA is reserved for patients who require a more advanced level of treatment planning, precision control, and long-term clinical supervision. While the underlying biological response of iris pigmentation remains consistent, XTRA differs from the standard Lumineyes protocol through its laser platform, energy management system, and overall treatment adaptability.
- Extended shot density and advanced parameter optimization
- Closer follow-up across treatment stages
- Commitment-based long-term clinical support
- The Lumineyes 9G plus laser device is used, which can target a wider iris area, has an extended duration of effect, and also offers increased safety.
Safety Considerations
Laser eye color change is designed to minimize risk by avoiding incision, foreign materials, and intraocular manipulation. Safety depends on correct patient selection, controlled application parameters, and appropriate follow-up evaluations. Clinical experience indicates that the absence of intraocular entry significantly reduces many of the risks associated with surgical procedures.
Key safety elements include:
- No surgical wound: reduces risk of infection or wound-related complications.
- No implant-related issues: eliminates risks of implant migration, endothelial contact or chronic inflammation.
- Anatomical preservation: corneal and internal structures remain unchanged.
- Controlled parameters: the laser operates within defined medical thresholds.
Patients are monitored throughout the process, and any variation in response is evaluated as part of the clinical protocol.
After the Procedure
Most individuals resume standard activities shortly after each session. Temporary light sensitivity or mild irritation may occur but usually resolves quickly. Sunglasses may provide comfort in the immediate period after treatment.
Typical observations include:
- Gradual brightening over time
- Mild, temporary sensitivity to light
- Stable long-term appearance once the modulation phase concludes
- No disruption of daily visual function
If any unexpected symptoms occur, patients are advised to contact their clinic for evaluation.
For a detailed, week-by-week explanation of what to expect after treatment, read our
laser eye color change recovery timeline.
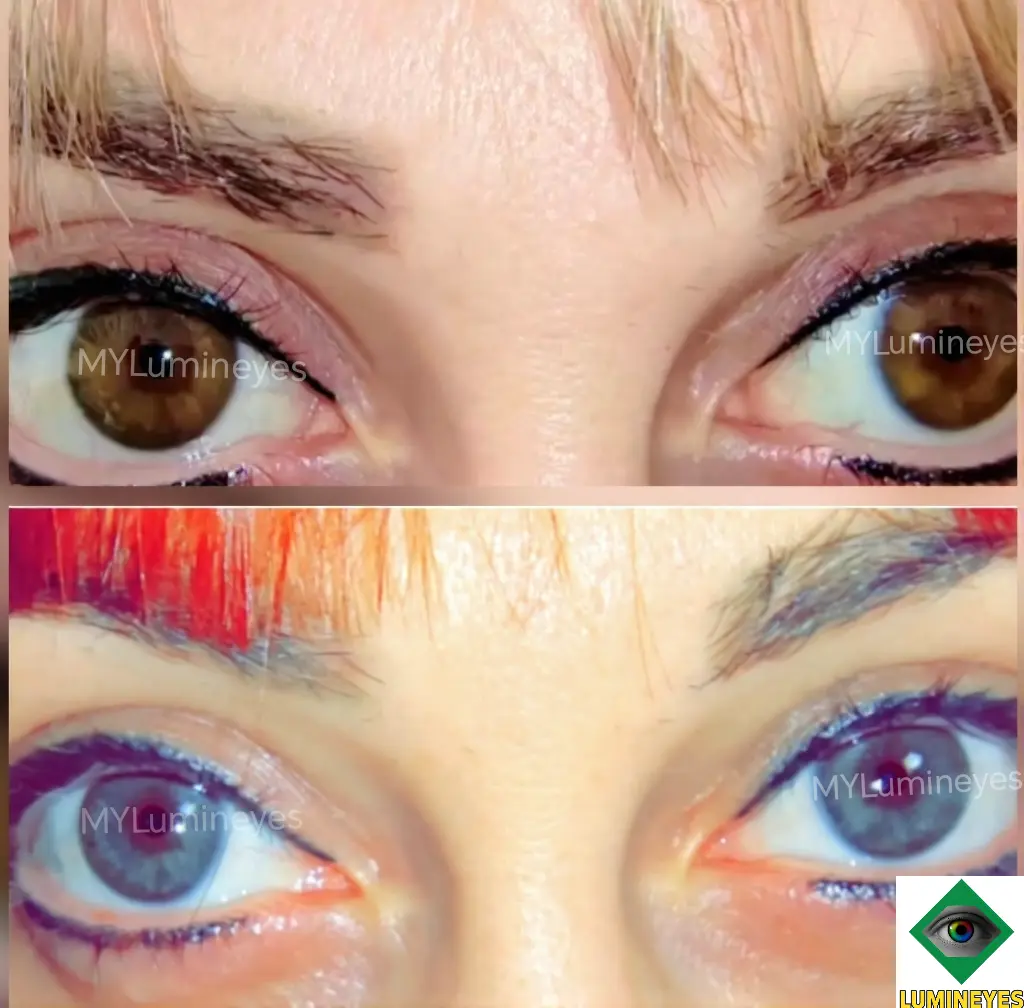
Comparison With Other Methods
Laser eye color change is a non-incisional medical approach and does not involve implants, corneal pigmentation techniques or intraocular prostheses. Its mechanism and safety profile differ fundamentally from surgical procedures, while maintaining the natural structure of the eye.
Clinical Experience & Predictability
Over more than a decade of clinical practice, consistent response patterns have been observed across thousands of eyes treated with the Lumineyes protocol. Although every iris is biologically unique, the staged laser modulation technique allows clinicians to evaluate pigment behavior at each step and adjust parameters within safe medical thresholds. This accumulated clinical experience forms the basis for anticipating how stromal pigment will respond over consecutive sessions, improving both safety and the predictability of outcomes.
Expert Insights: What Determines a Predictable Laser Response?
The clinical predictability of laser eye color change depends on a combination of anatomical, biological and optical factors. Understanding these parameters helps explain why outcomes vary between individuals, even when the same laser protocol is used.
- Iris stromal thickness: The density and depth of pigment layers affect how the laser interacts with melanin granules.
- Melanin composition: The ratio of eumelanin to pheomelanin influences the speed and uniformity of brightening.
- Cellular clearance rate: Natural metabolic variations determine how quickly pigment fragments are removed.
- Iris vascular microenvironment: Subtle differences in perfusion may influence biological response patterns.
- Optical scattering properties: Once melanin decreases, light reflection and scattering reveal underlying iris texture.
These parameters do not affect the safety of the treatment but help clinicians anticipate how each eye may respond across consecutive sessions.
Common Misconceptions About Laser Eye Color Change
“The laser burns or removes iris tissue.”
No. The method is non-incisional and does not burn, cut or remove any tissue. It modulates pigment through a controlled photochemical effect.
“Results are immediate.”
The brightening effect is gradual. Most visible changes occur over weeks as melanin fragments clear naturally.
“The eye color becomes artificial or flat.”
Because the iris texture remains unchanged, final results preserve natural patterns rather than producing a synthetic appearance.
“It is the same as corneal pigmentation or implants.”
No. Laser eye color change does not alter corneal tissue or introduce foreign material. It is biologically distinct from surgical or pigment-implant methods.
“One session is enough.”
Most patients require multiple sessions for uniform brightening. The number depends on baseline pigmentation.
How the Process Works: A Text-Based Graphic Explanation
The following step-by-step outline provides a clear, visualization-style explanation without using images:
1. Natural iris pigment (melanin) absorbs light. 2. The laser delivers a controlled wavelength to the stromal layer. 3. Melanin granules fragment into smaller particles. 4. The eye's natural metabolic system begins clearance. 5. Light scattering increases as pigment density decreases. 6. The iris appears progressively lighter and more reflective.
This simplified model mirrors the biological sequence observed during the modulation phase and helps patients understand why the results unfold gradually over time.
Conclusion
Laser eye color change is a non-incisional medical method that works with the eye’s natural pigment to achieve a gradual, controlled and natural-looking brightening of the iris. Its safety profile and anatomical preservation distinguish it from surgical alternatives. Individuals considering this option should undergo a full ophthalmic evaluation to determine suitability and expected outcomes.
Clinical Questions & Answers
How much does the procedure cost?
Cost depends on iris pigmentation density and the number of required sessions. A clinical evaluation is required to determine an individualized treatment plan and total cost.
How many sessions are required?
Session number varies based on baseline pigment and desired brightness. Treatment is staged and determined after ophthalmic evaluation.
Am I eligible for the procedure?
Eligibility is confirmed after full ophthalmic assessment, including iris structure, pigment distribution, and overall ocular health.
How do I book a clinical evaluation?
You can request a clinical evaluation through the booking form. Our medical team will respond with assessment details and next steps.
How long is the recovery period?
Most patients resume daily activities shortly after each session. Brightening develops gradually over weeks as pigment clears naturally.
Will the procedure affect my vision?
Most patients maintain normal daily vision. Temporary light sensitivity can occur after sessions and is monitored during follow-up.
What is Lumineyes® XTRA?
Lumineyes® XTRA is an advanced protocol reserved for selected patients who require extended planning and closer clinical monitoring. It is offered only after detailed ophthalmic evaluation.
Clinical Overview of the Lumineyes® Method (Video)
This short clinical video provides a visual explanation of how controlled laser energy interacts with iris melanin during the Lumineyes® procedure. It is intended for educational purposes and helps patients understand the biological process behind gradual iris lightening. Individual responses may vary.
The American Academy of Ophthalmology has issued warnings about two cosmetic eye color–changing procedures: artificial iris implants and keratopigmentation. These techniques may cause glaucoma, corneal damage or vision loss and should not be performed on healthy eyes.
Related Topics for a Full Understanding
Understanding laser eye color change is easier when viewed within the wider context of other eye color–related topics:
- Readers seeking a comparative overview may also explore Eye Color Change Surgery, while those interested in broader biological mechanisms may refer to Permanent Eye Color Change.
- “For a step-by-step explanation, see our How to Change Eye Color With Laser guide.”
- “If you have had previous eye surgery or other aesthetic procedures, you can review our Patient Eligibility Information before scheduling an evaluation.”
- Laser Eye Color Change Procedure (Official Page)
- 👉 Clinical documentation is available in our Research section (PDF).
- Author background and related academic publications are available via Google Scholar.
Important disclaimer: This page summarizes current clinical experience and research but does not guarantee outcomes or replace a personalized medical recommendation. All decisions about laser eye color change must be made together with a qualified ophthalmologist after a full examination.

